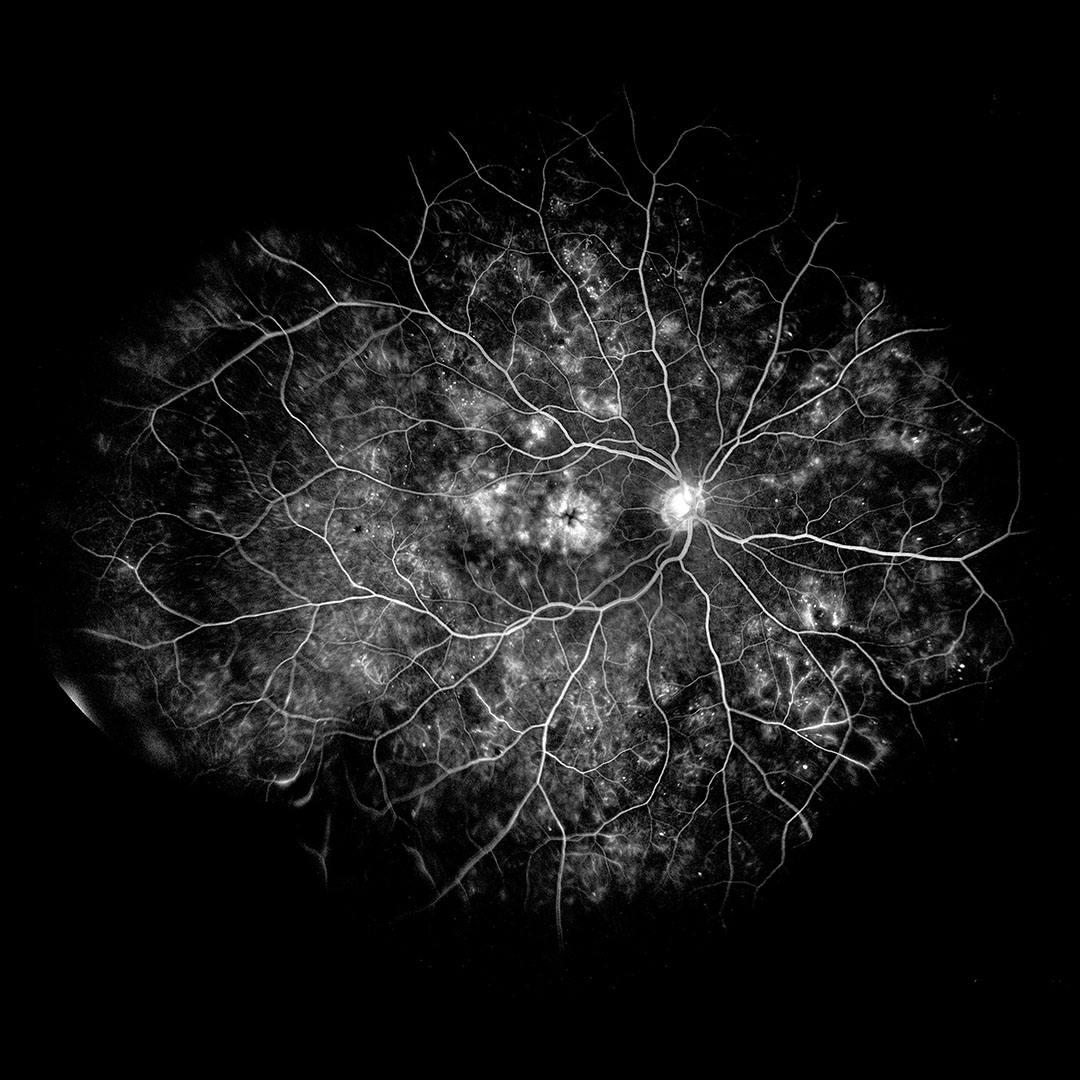
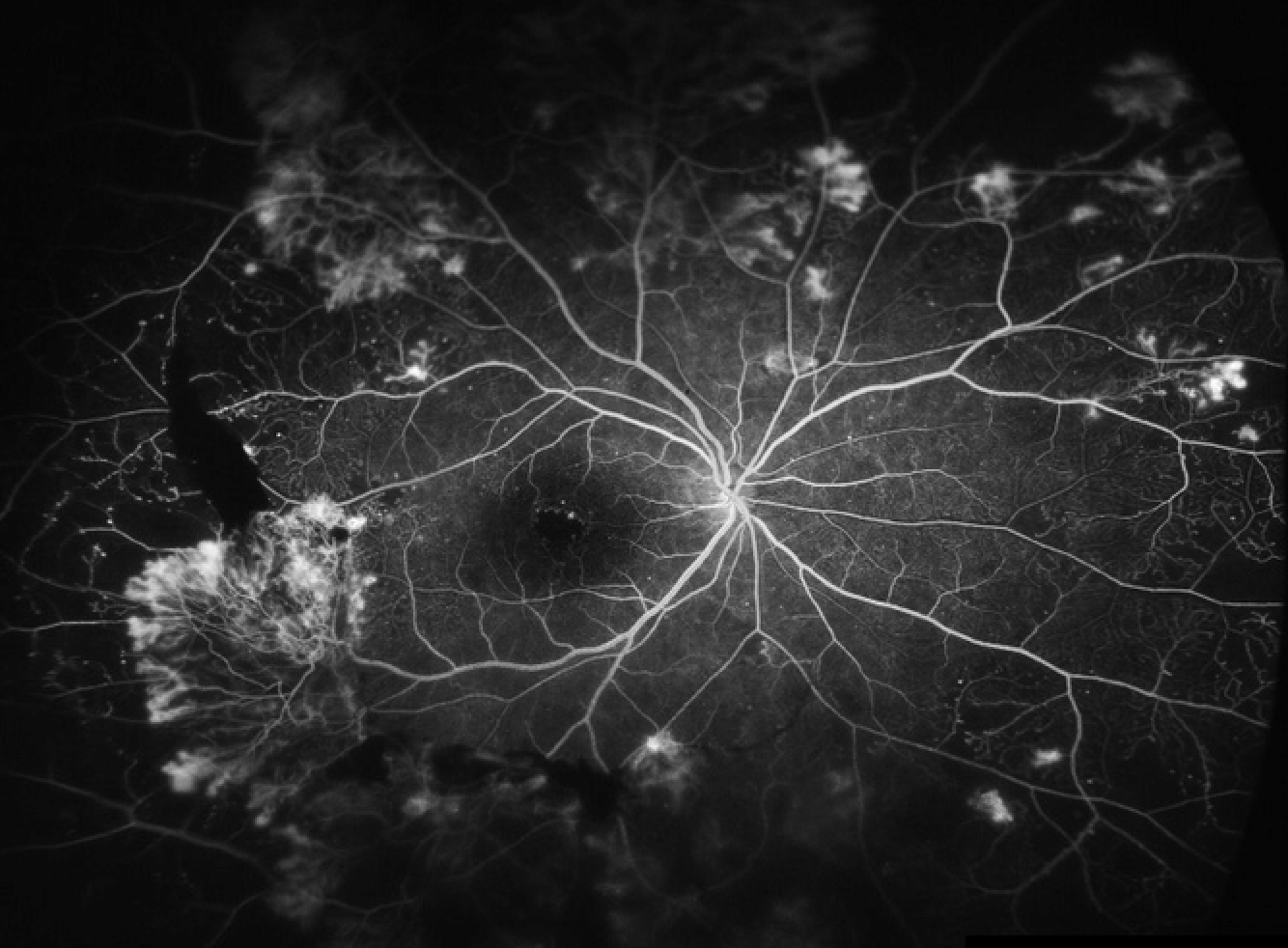
Fluorescein Angiography
What is Fluorescein Angiography?
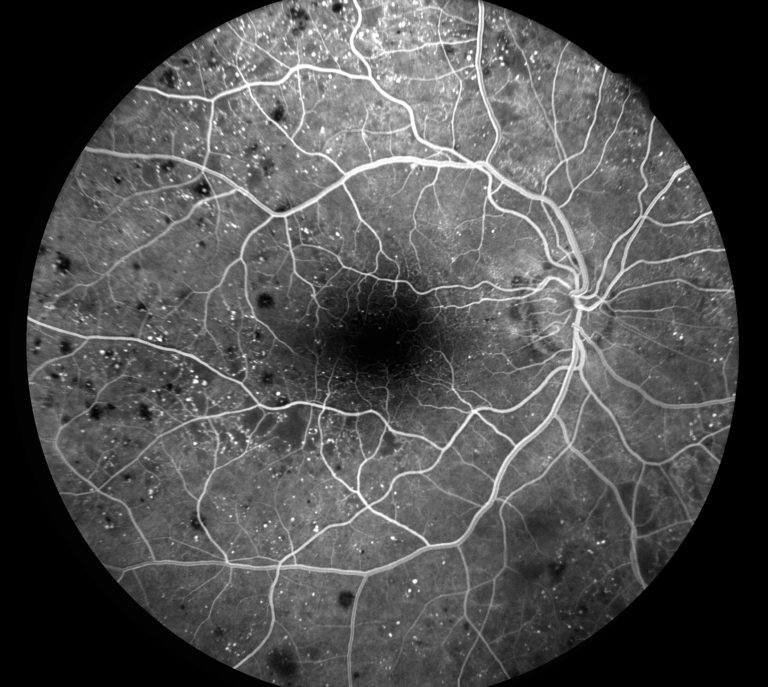
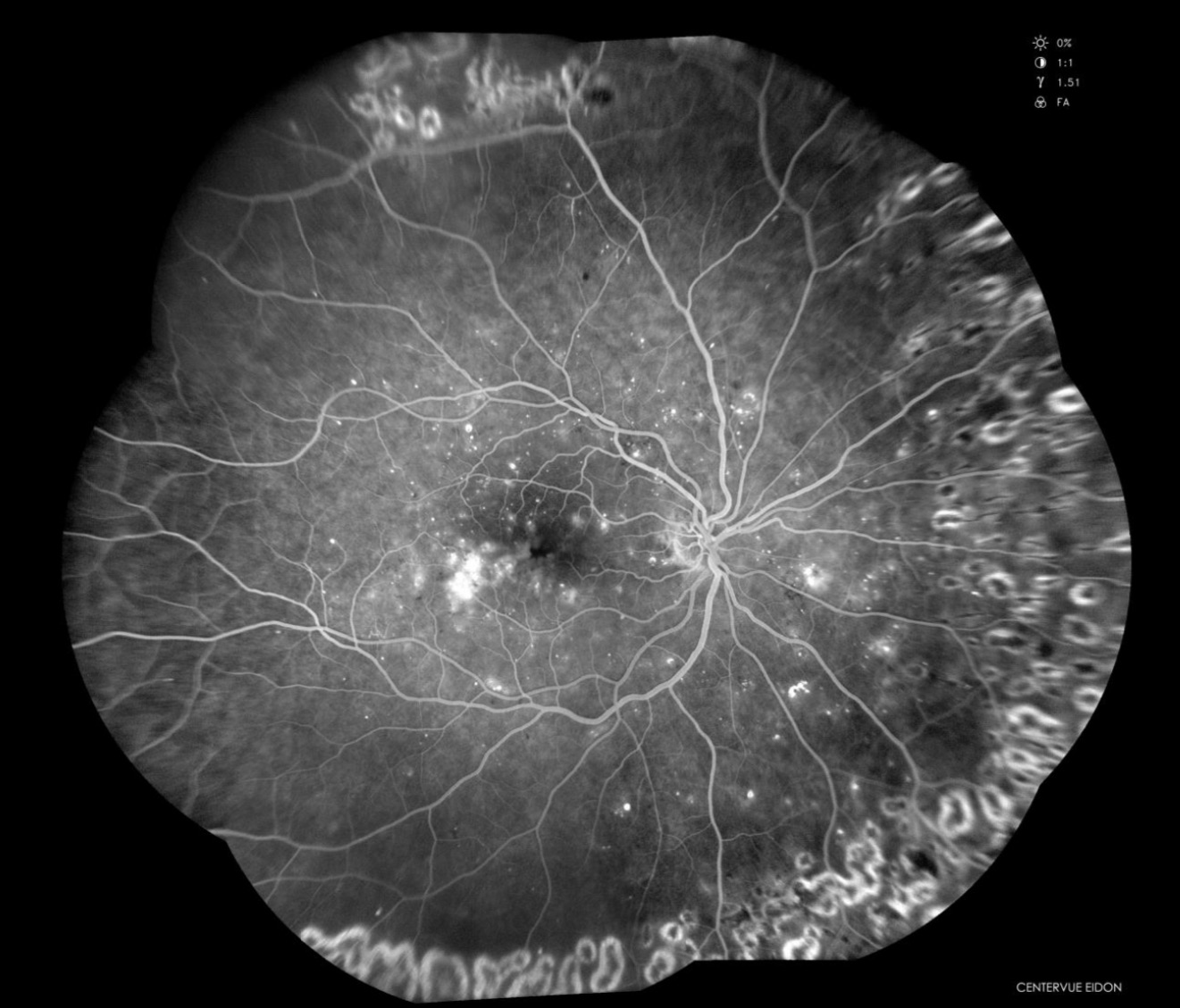
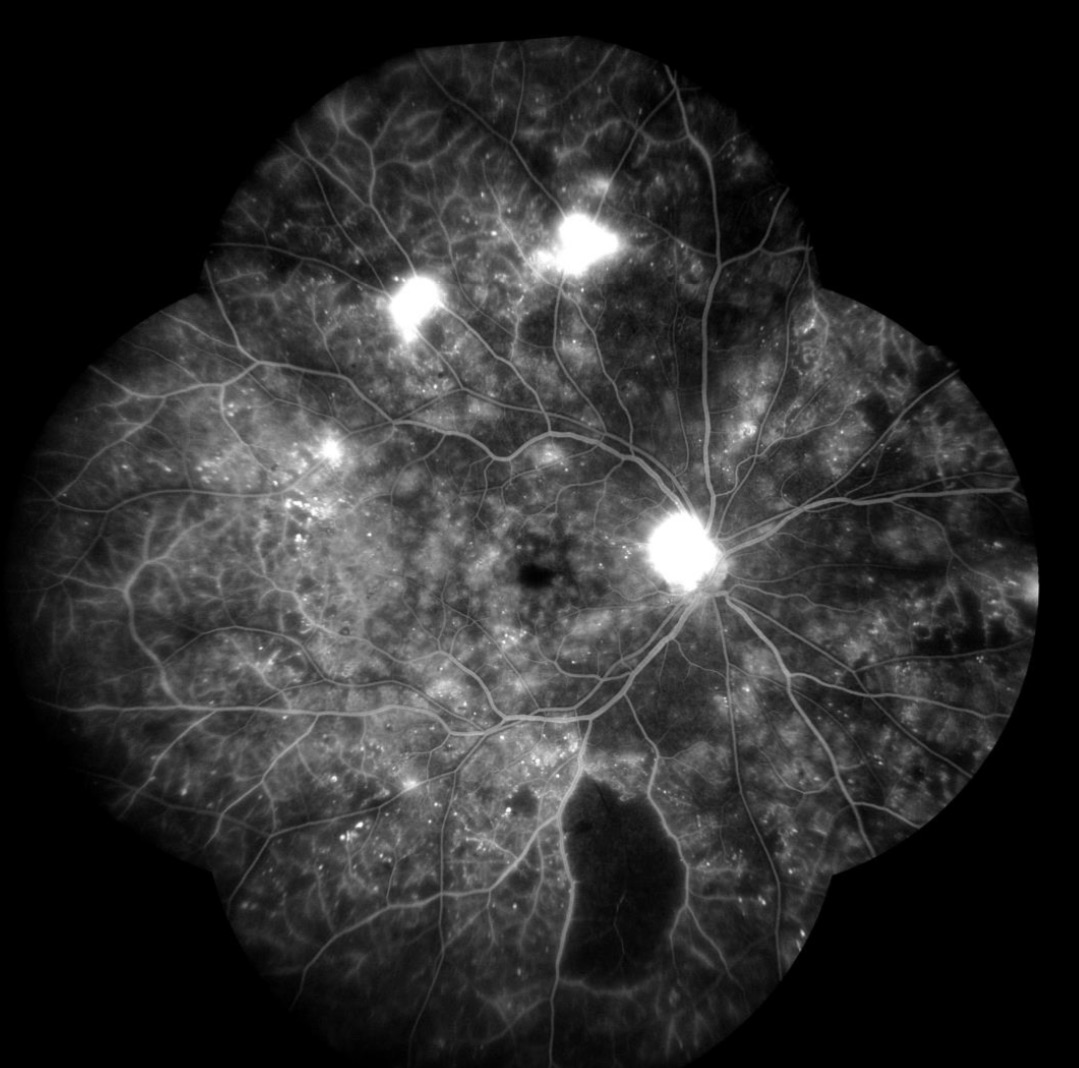
Fluorescein angiography (FA) is a diagnostic imaging technique used to evaluate the blood flow and circulation within the retina and choroid of the eye. It involves the injection of a fluorescent dye called fluorescein into a vein, typically in the arm, followed by the capture of sequential photographs as the dye circulates through the blood vessels in the eye. This procedure provides valuable information about the integrity, perfusion, and abnormalities of the retinal and choroidal vasculature.
Fundamentals of Fluorescein Angiography
Here’s how fluorescein angiography works and its significance in clinical practice:
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient’s pupils are dilated with eye drops to facilitate imaging of the retina. The patient is positioned in front of a specialized camera equipped with filters that allow for the visualization of fluorescein dye.
- Injection of fluorescein dye: A small amount of fluorescein dye is injected into a vein, usually in the arm. The dye quickly circulates through the bloodstream and reaches the blood vessels in the eye within seconds.
- Image capture: As the fluorescein dye flows through the retinal and choroidal blood vessels, sequential photographs are taken at rapid intervals using the fundus camera. The camera captures images of the dye as it passes through the blood vessels, highlighting areas of normal perfusion as well as any abnormalities or blockages.
- Analysis: The captured images are then analyzed by retinal specialists. They examine the images for signs of retinal pathology, such as areas of leakage, blockage, or abnormal blood vessel growth. Fluorescein angiography provides detailed information about the structure and function of the retinal vasculature, helping to diagnose and monitor conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, retinal vein occlusions, retinal artery occlusions, and uveitis.
- Treatment planning: Fluorescein angiography plays a crucial role in treatment planning for retinal and choroidal disorders. By identifying areas of abnormal blood flow or leakage, it helps clinicians determine the most appropriate treatment interventions, such as laser therapy, intravitreal injections, or surgical procedures. It also allows for targeted delivery of treatment to specific areas of pathology, maximizing efficacy and minimizing potential side effects.
- Monitoring: Serial fluorescein angiograms can be used to monitor the progression of retinal diseases and the response to treatment over time. By comparing images taken at different time points, clinicians can assess changes in retinal perfusion, identify new areas of pathology, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Overall, fluorescein angiography is a valuable diagnostic tool in ophthalmology, providing detailed information about retinal and choroidal blood flow and enabling visualization of vascular abnormalities that can help the diagnosis, treatment, and management of certain retinal diseases. Its ability to visualize vascular abnormalities and guide treatment decisions makes it an indispensable asset in the evaluation, management and follow up of certain retinal conditions.