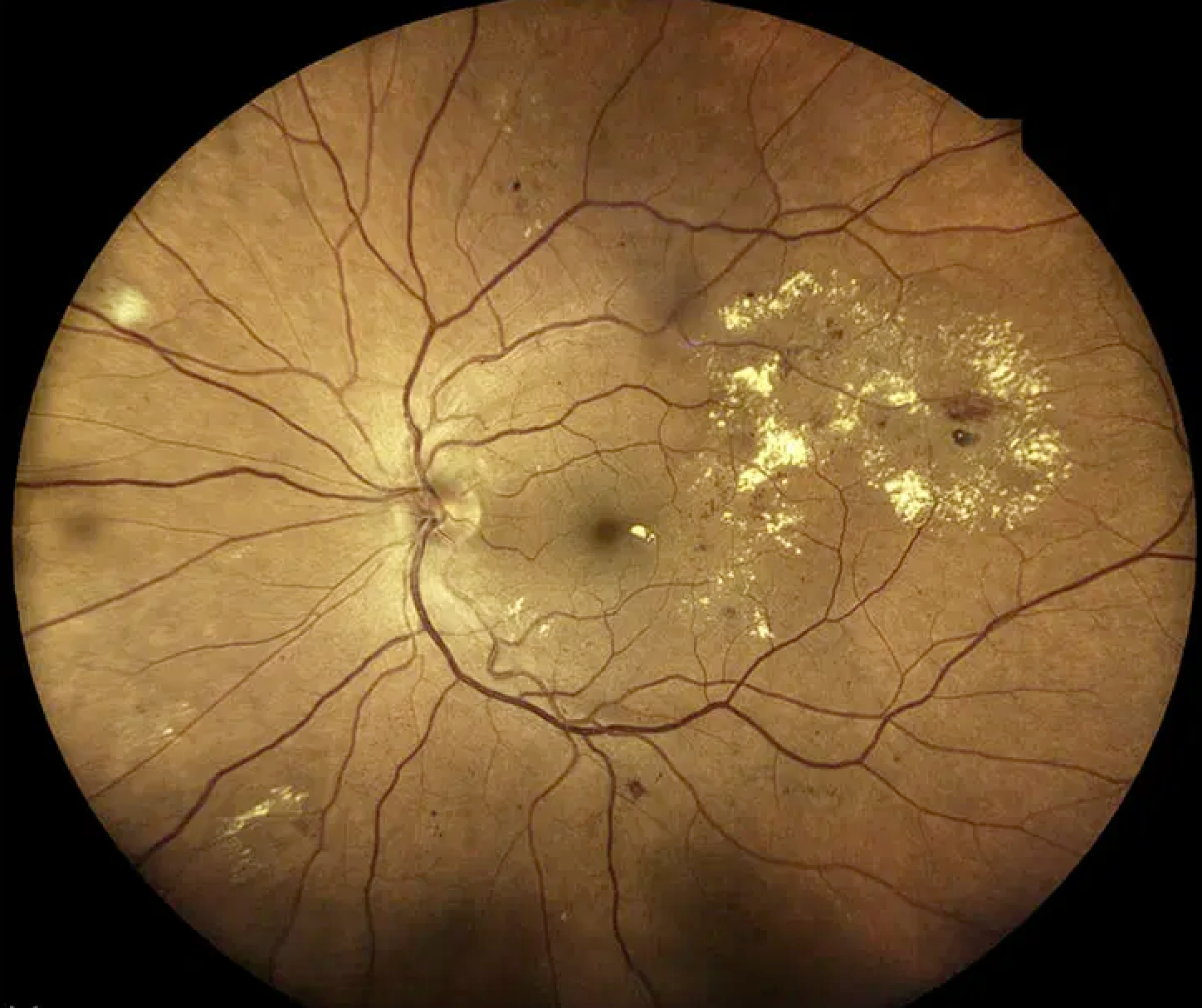
Diabetic Macular Edema
What is Diabetic Macular Edema?
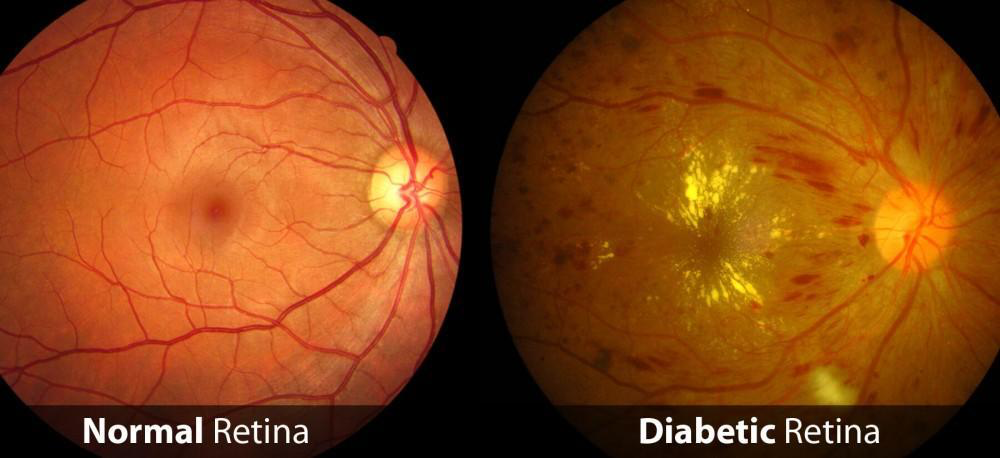
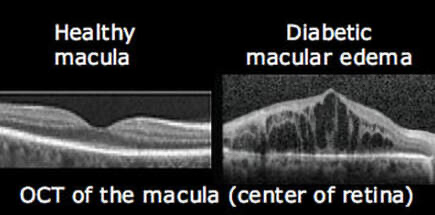
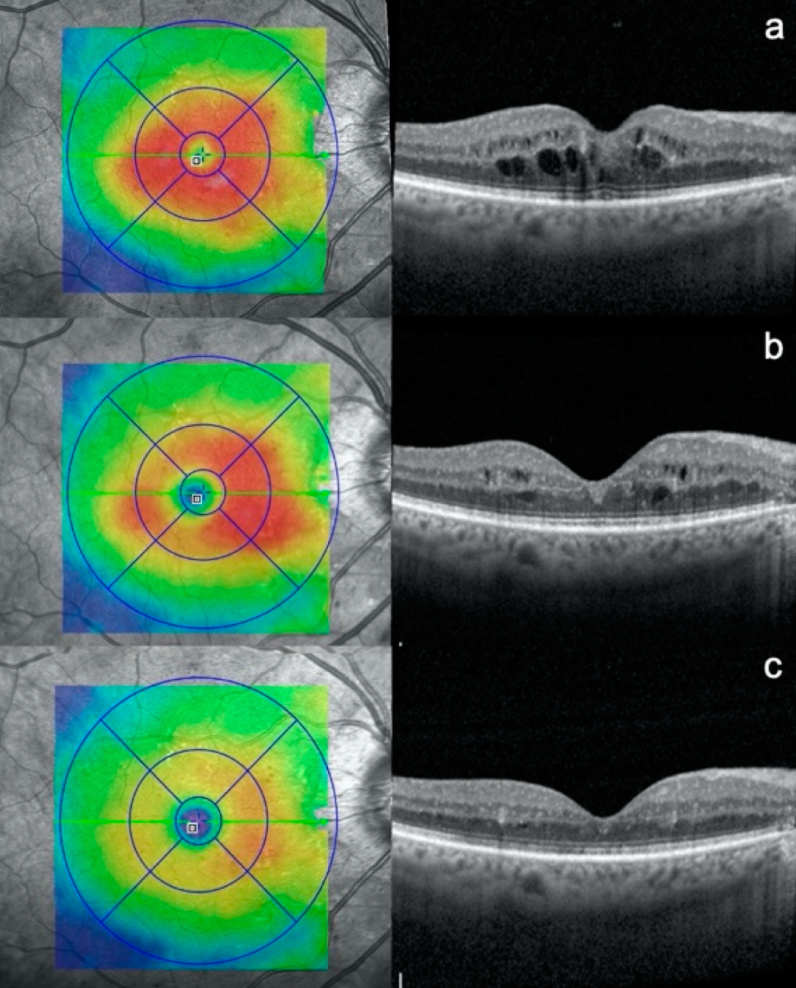
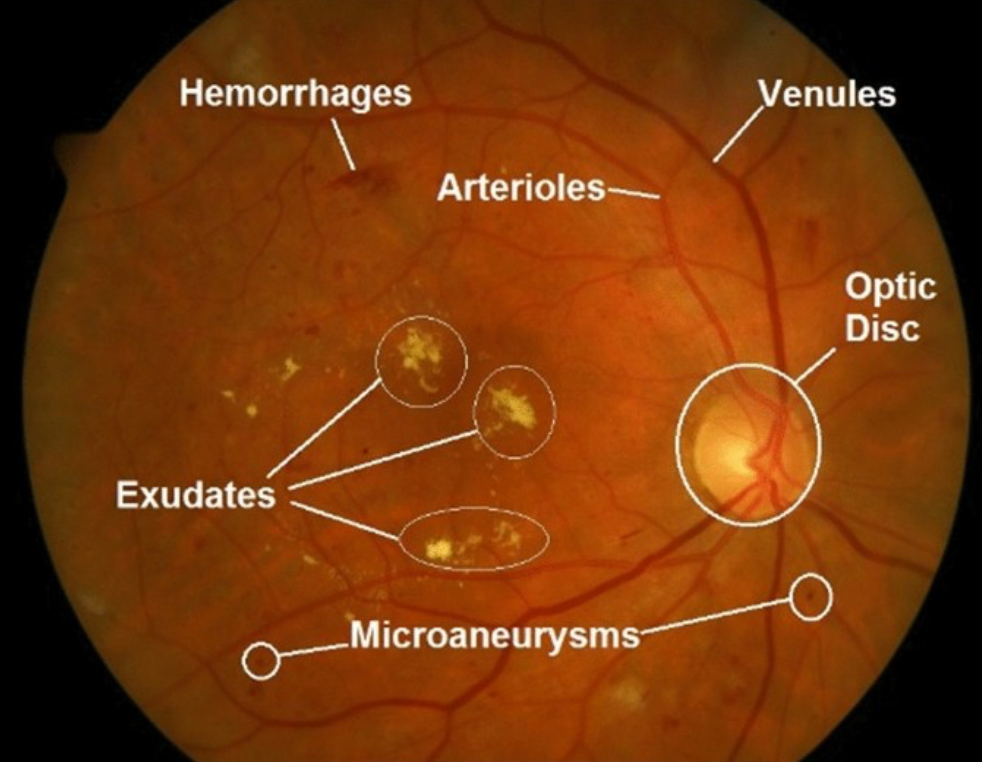
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication of diabetic retinopathy that specifically affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. In DME, fluid accumulates in the macula, causing it to swell and thicken, which can lead to blurry or distorted vision.
Treatments for Diabetic Macular Edema
The treatment of diabetic macular edema aims to reduce swelling in the macula and preserve or improve vision. Here are some common treatment options
- Anti-VEGF injections: Medications called anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drugs are injected into the eye to help reduce swelling and leakage from abnormal blood vessels. These injections can help improve vision and prevent further damage to the macula. Examples of anti-VEGF drugs include, aflibercept (Eylea), and bevacizumab (Avastin).
- Laser therapy: Focal laser photocoagulation can be used to treat DME by sealing leaking blood vessels in the retina. This helps reduce swelling and prevent further fluid accumulation in the macula. Laser treatment is often used in combination with anti-VEGF injections or as a standalone therapy, depending on the severity and location of the edema.
- Corticosteroid injections: In some cases, corticosteroid medications may be injected into the eye to help reduce inflammation and swelling in the macula. These injections can be effective in improving vision in individuals with DME, particularly when anti-VEGF therapy is not suitable or effective.
- Surgery: In cases of severe diabetic macular edema that do not respond to other treatments, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be considered. During vitrectomy, the vitreous gel in the eye is removed to allow for better visualization and treatment of the macula. This procedure may be combined with other treatments such as membrane peeling or laser therapy.
- Control of diabetes and other risk factors: Tight control of blood sugar levels, as well as management of other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol, is important in preventing and managing diabetic macular edema. Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication adherence, can help reduce the risk of vision loss and other complications associated with DME.
Individuals with diabetes should undergo regular eye exams to monitor for diabetic macular edema and other complications of diabetic retinopathy. Early detection and timely treatment are essential in preserving vision and preventing further damage to the macula.