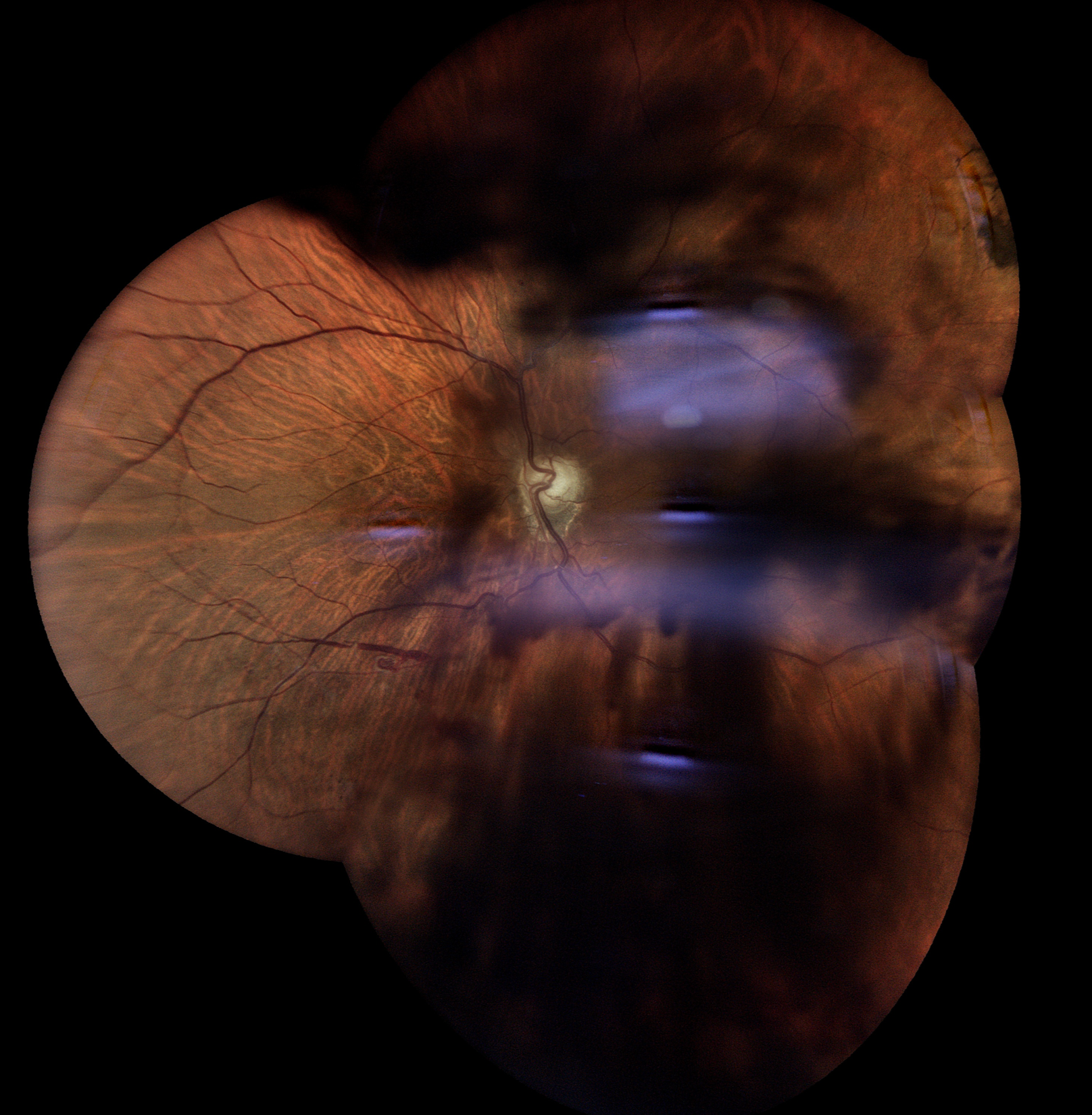
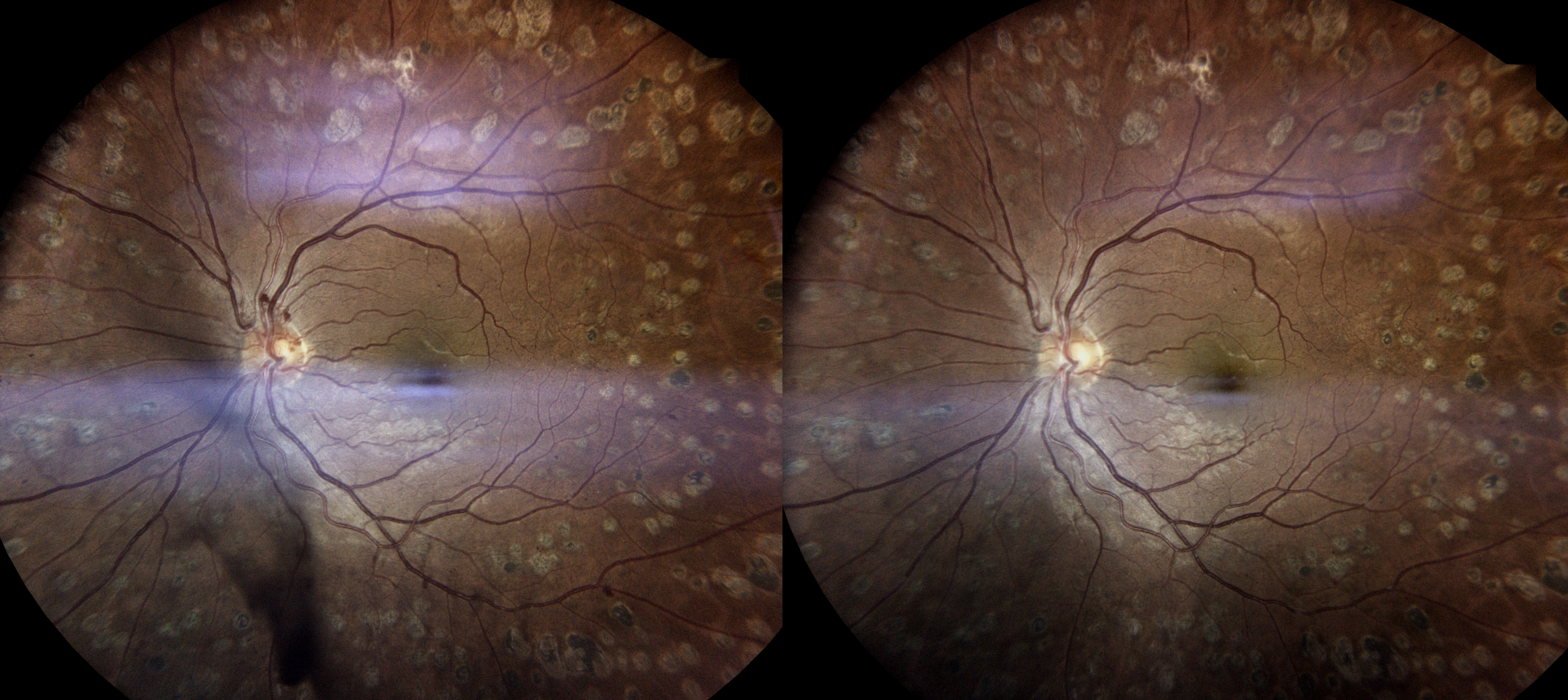
Vitreous Hemorrhage
What is a Vitreous Hemorrhage?
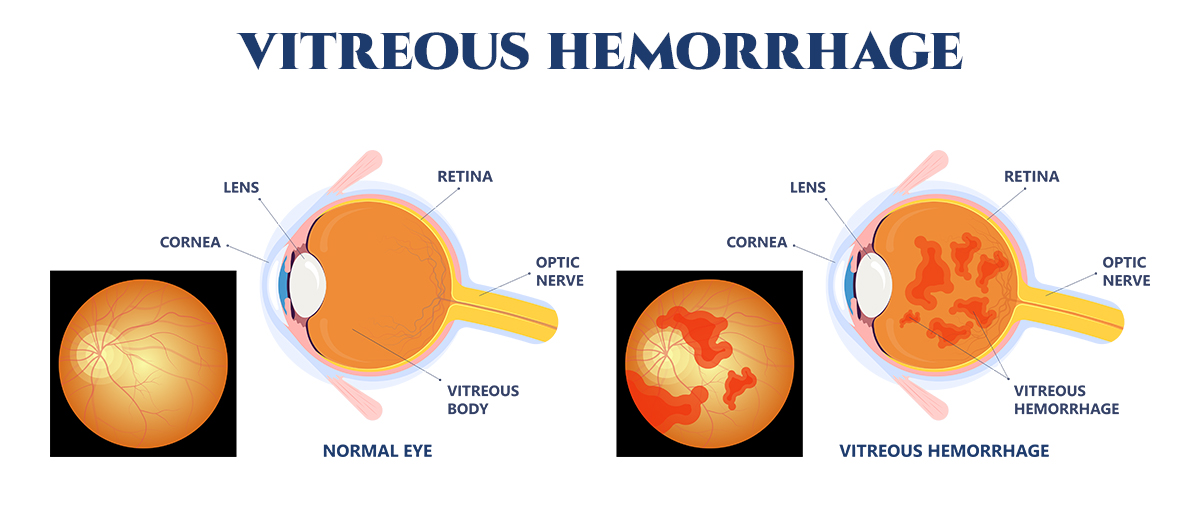
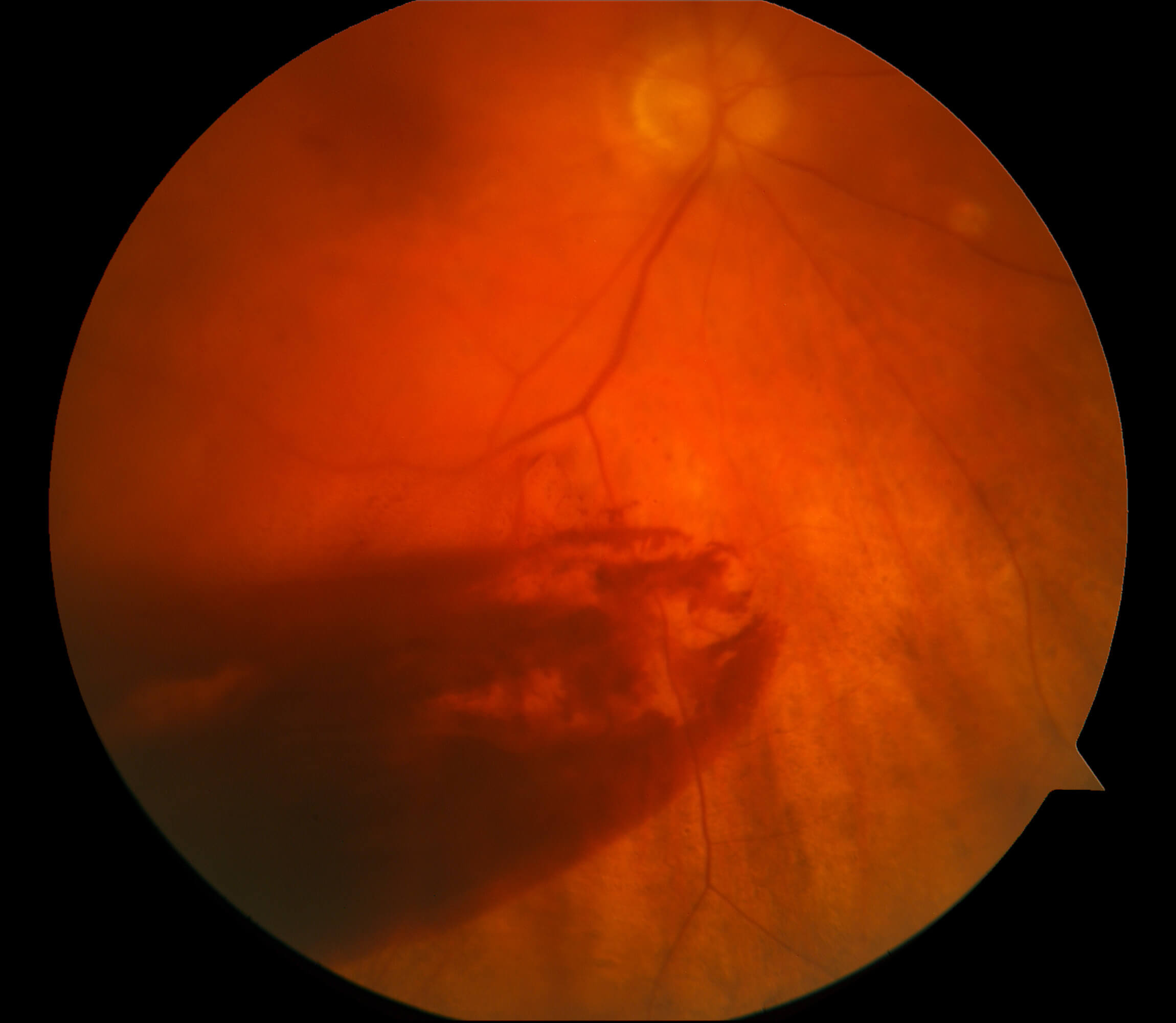
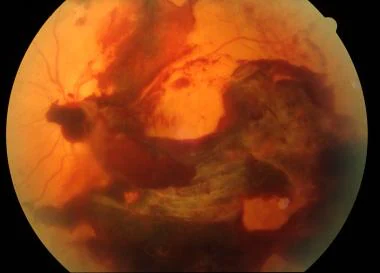
A vitreous hemorrhage refers to bleeding into the vitreous humor, the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eye.
Causes of a vitreous hemorrhage include:
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Damage to the retinal blood vessels due to diabetes can lead to bleeding into the vitreous humor.
- Retinal Tears or Detachments: Tears in the retina can cause bleeding from the torn vessels.
- Trauma: Injury to the eye can result in bleeding into the vitreous humor.
- Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD): As the vitreous humor pulls away from the retina, it can cause small blood vessels to tear and bleed.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Wet AMD can lead to the growth of abnormal blood vessels that bleed.
- Blood Vessel Abnormalities: Conditions like retinal vein occlusion or neovascularization can lead to vitreous hemorrhage.
Symptoms of Vitreous Hemorrhage
Key symptoms to look out for a vitreous hemorrhage include:
- Sudden appearance of floaters or dark spots
- Reduced vision, often described as a “fog” over the field of vision
- In severe cases, loss of vision
Treatments for Vitreous Hemorrhage
Treatment options include:
- Observation: Small hemorrhages may resolve on their own over time. Regular monitoring by a retina specialist is essential.
- Medical Management:
- Anti-VEGF Injections: These are used particularly in cases related to neovascularization (e.g., diabetic retinopathy, AMD).
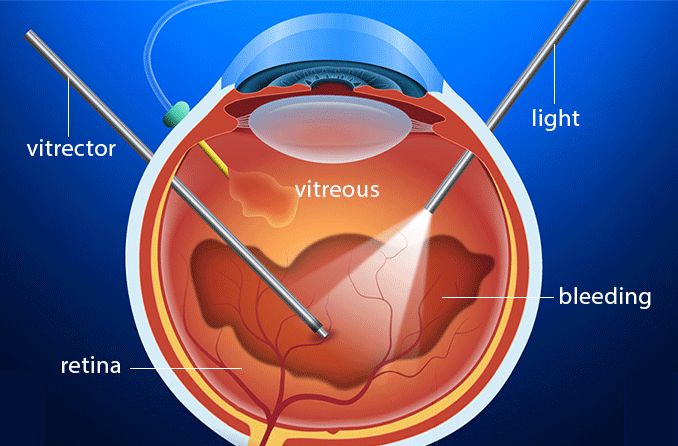
- Vitrectomy: Surgical removal of the vitreous gel is considered if the hemorrhage does not clear on its own or if it is severe. During this procedure, the vitreous humor is removed and usually replaced with a saline solution.
- Laser Therapy: Photocoagulation can be used to seal off bleeding vessels in conditions like diabetic retinopathy.
Prevention for Vitreous Hemorrhage
There are some prevention methods one can use to avoid a vitreous hemorrhage:
- Control of Underlying Conditions: Managing diabetes, hypertension, and other systemic conditions is crucial.
- Regular Eye Exams: Especially for individuals with risk factors like diabetes or a history of retinal problems.
- Protective Eyewear: To prevent trauma-related vitreous hemorrhages, particularly in high-risk activities or sports
Prognosis for Vitreous Hemorrhage
The outlook depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the hemorrhage. While many vitreous hemorrhages resolve without long-term damage, some may lead to complications like retinal detachment or permanent vision loss if not properly managed. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preserving vision.