Diabetic Retinopathy
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
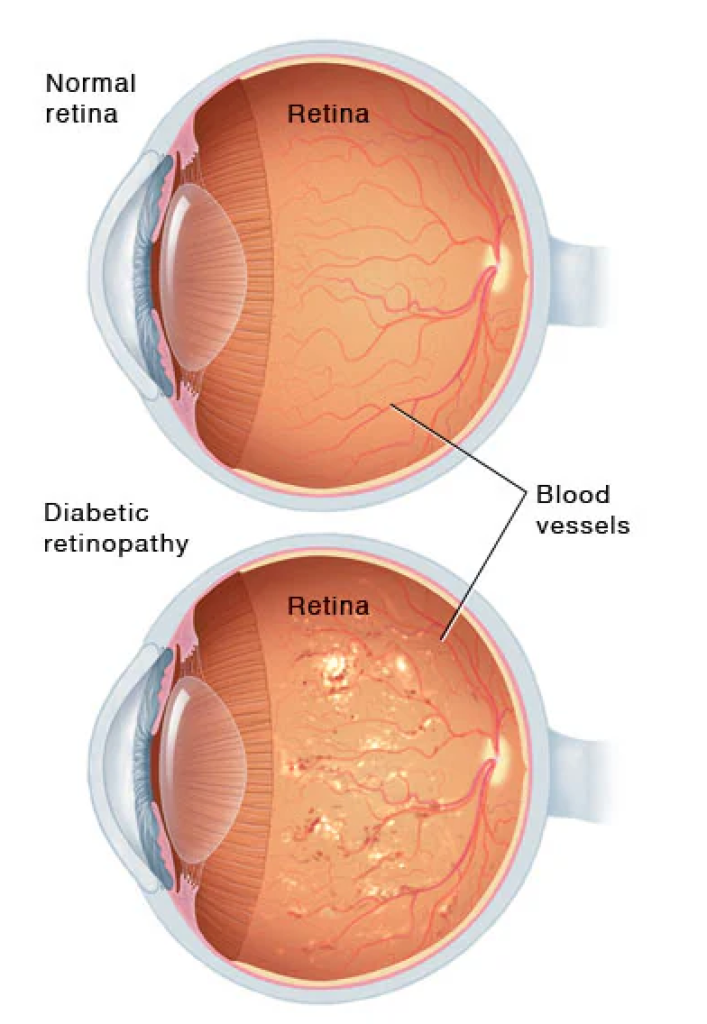
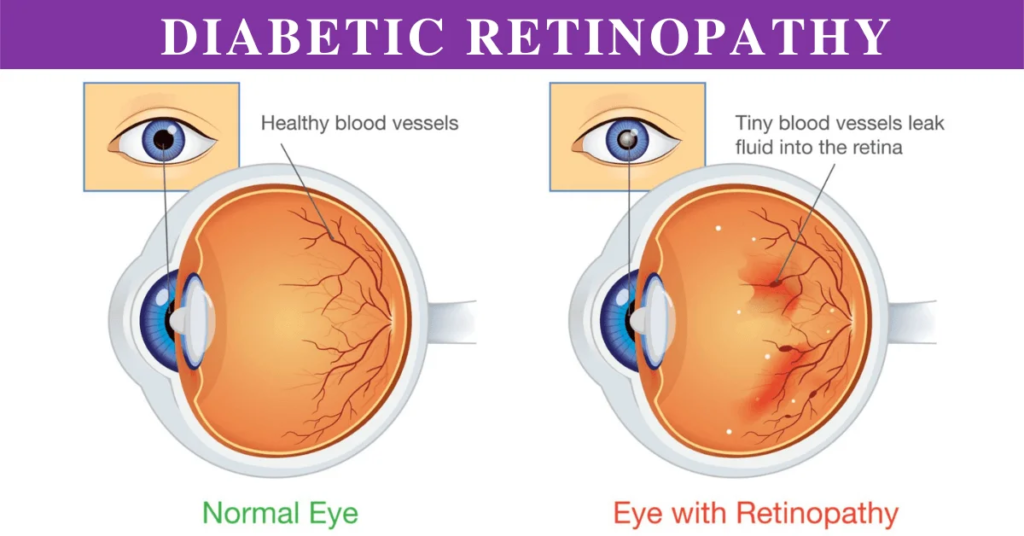
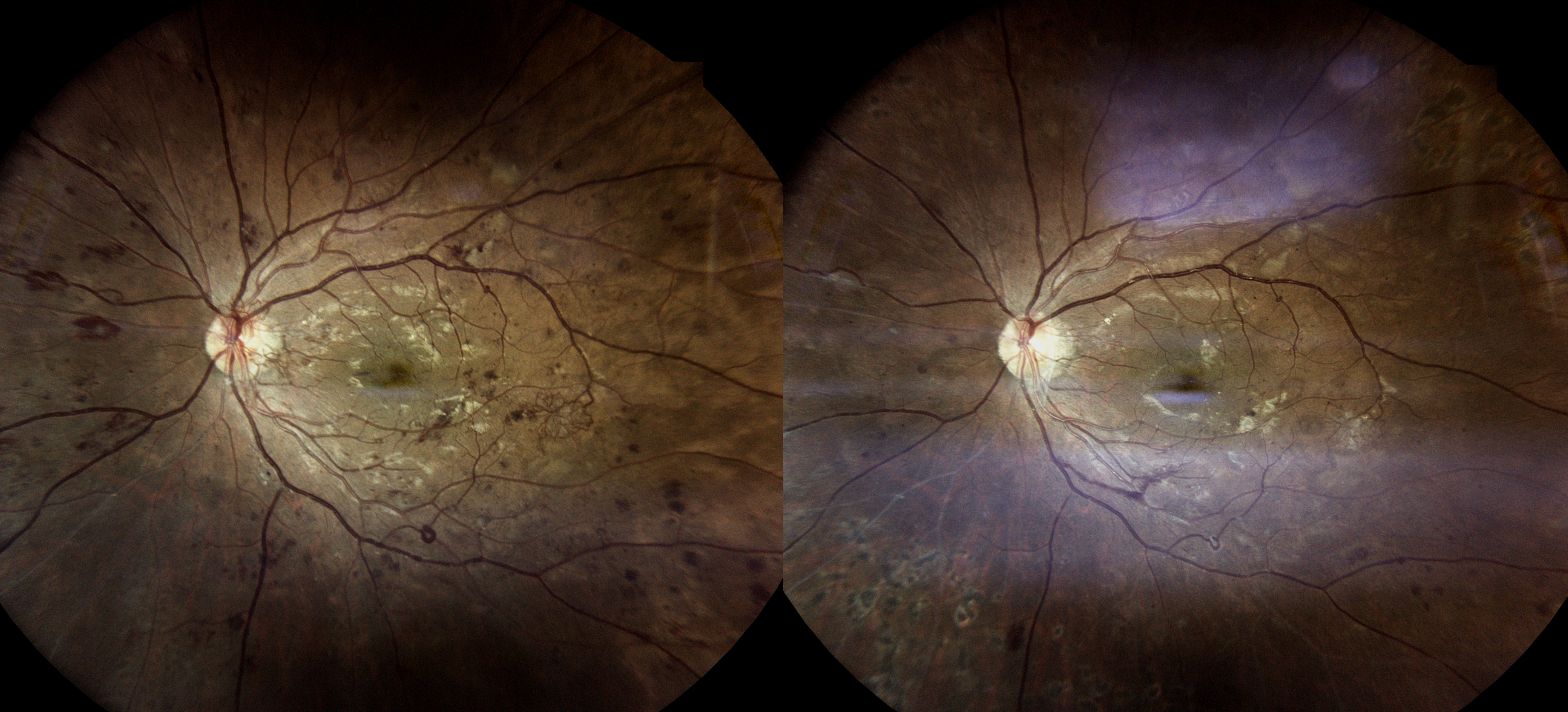
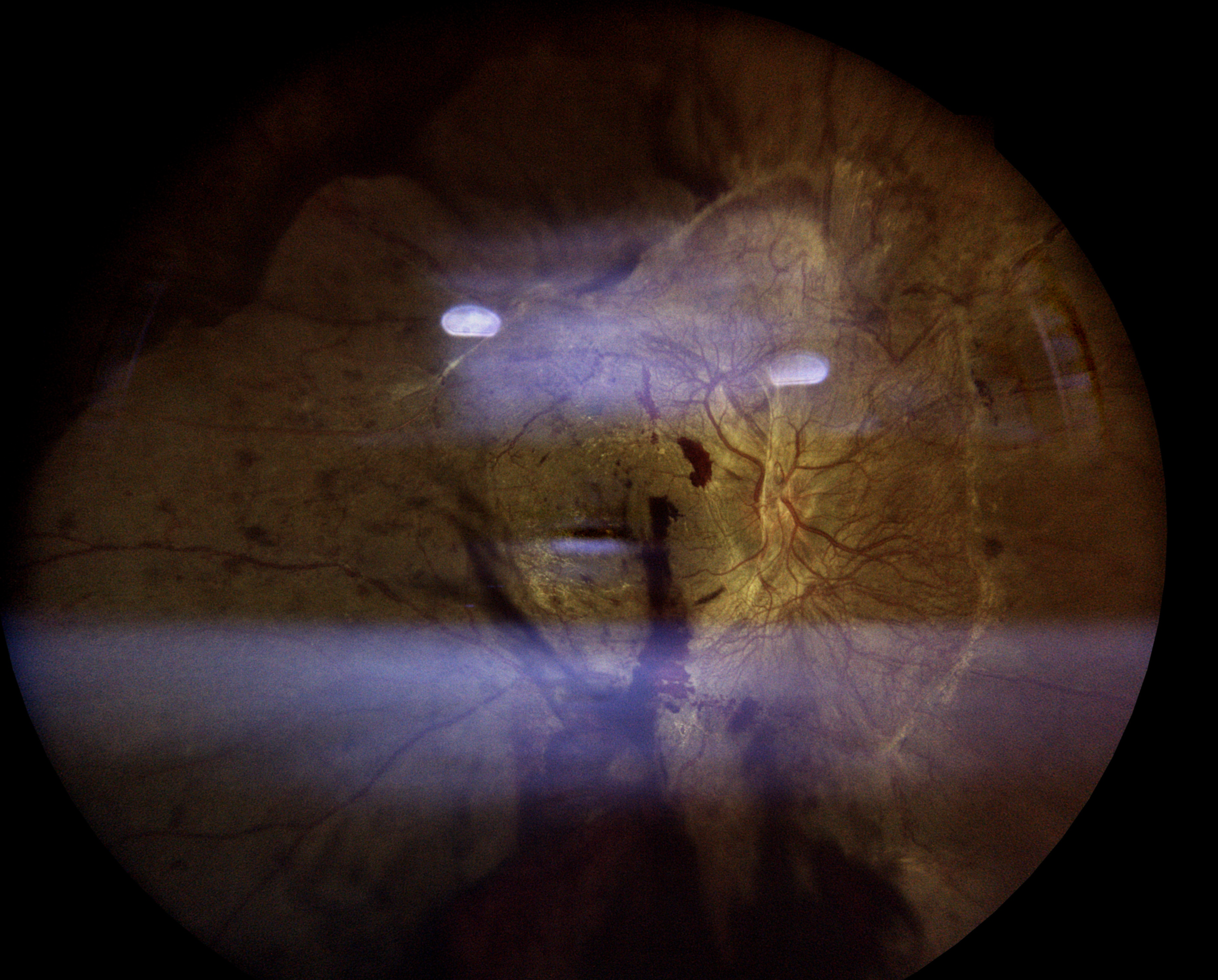
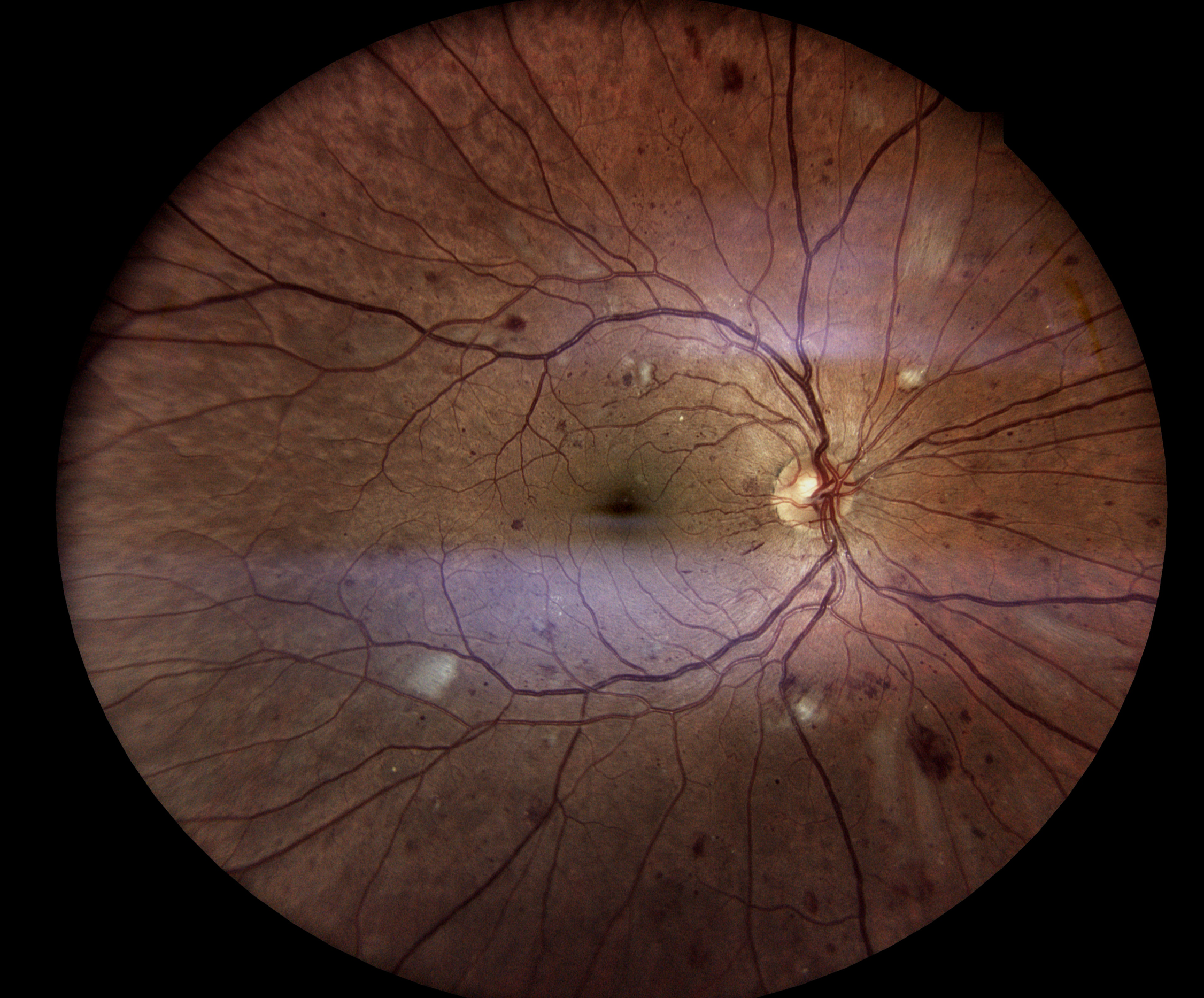
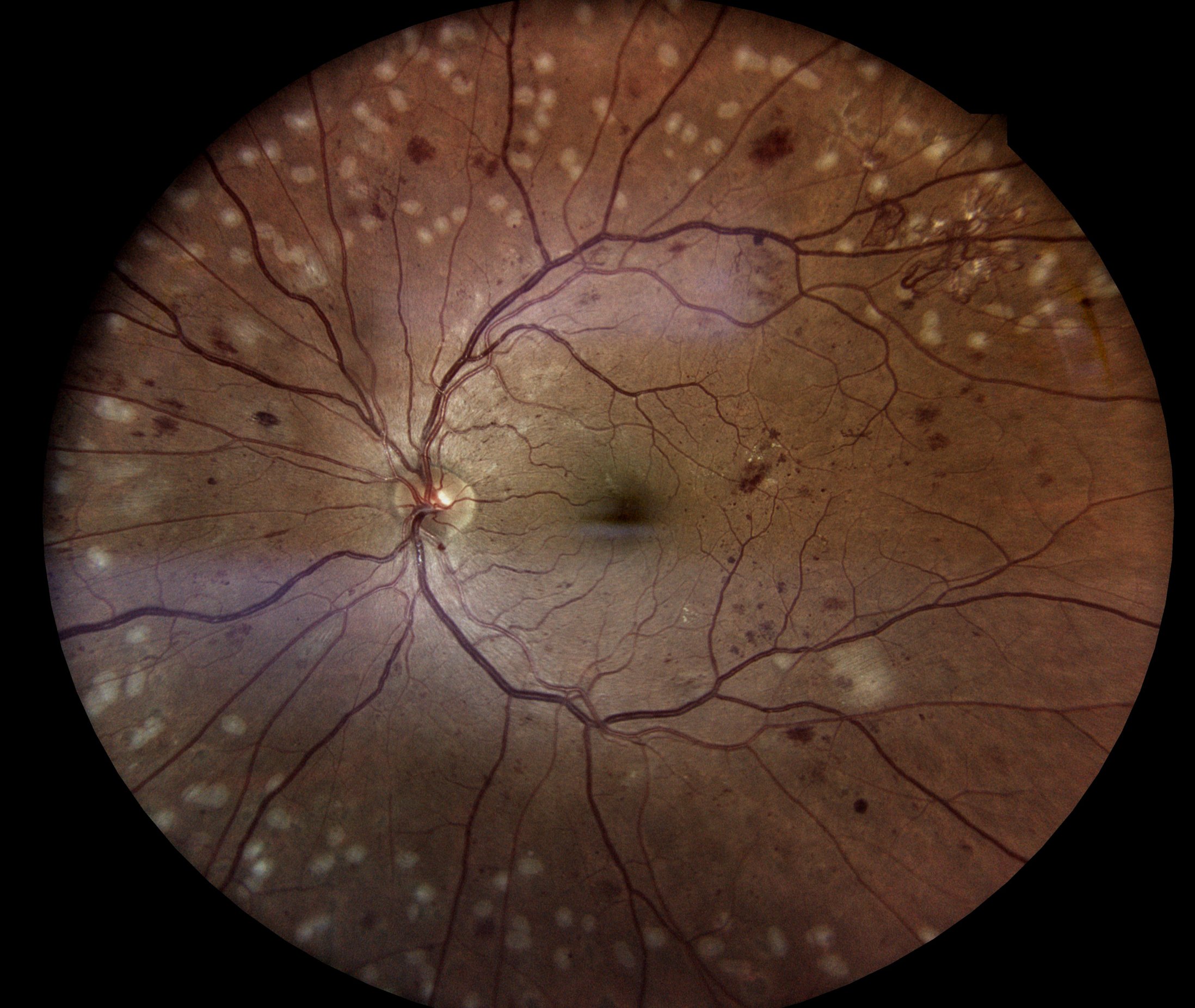
Diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that affects the eyes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, this damage can lead to vision problems and even blindness if left untreated.
There are two main types of diabetic retinopathy:
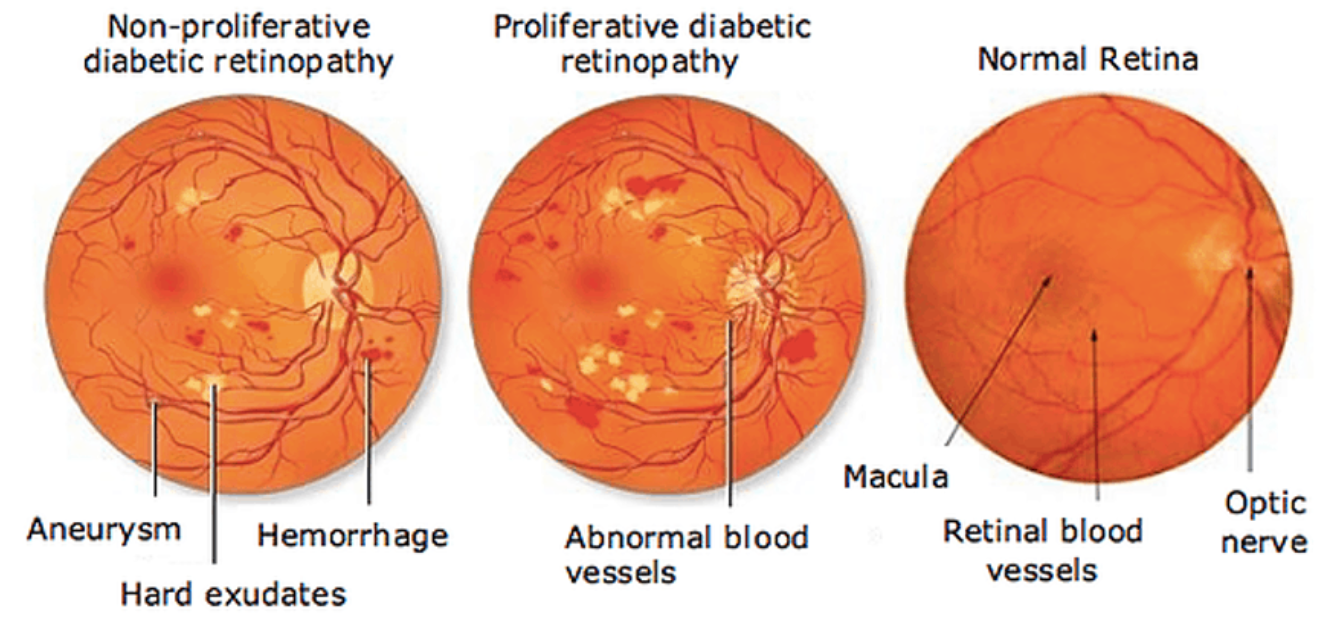
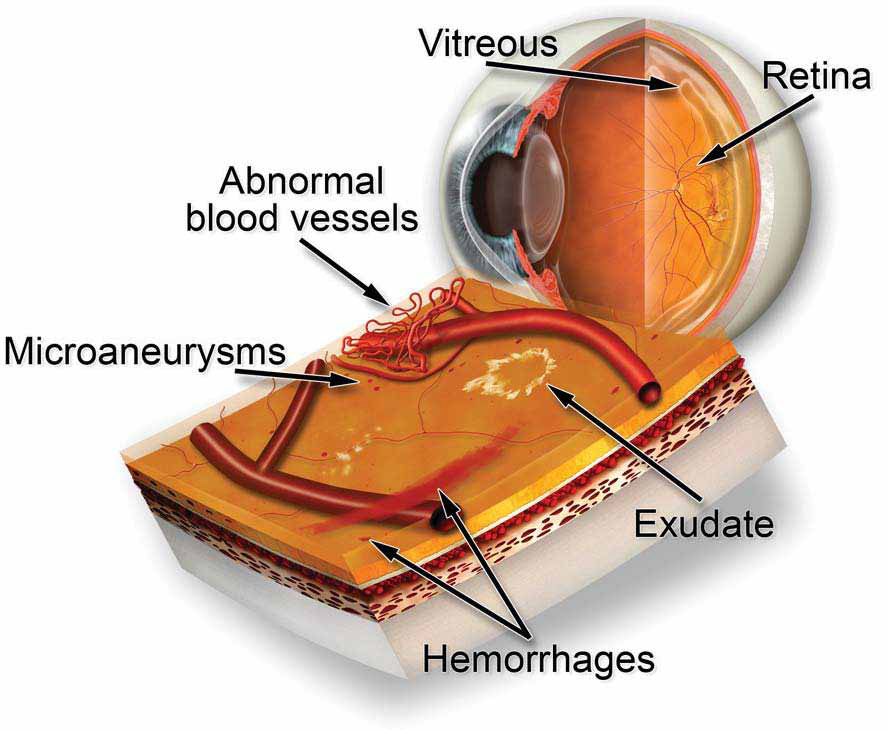
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR): In this early stage, small blood vessels in the retina leak fluid or blood, causing the retina to swell or form deposits called exudates.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): This advanced stage occurs when new, abnormal blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina. These blood vessels are fragile and can leak blood into the vitreous gel, leading to vision loss or blindness.
Treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition:
- Monitoring: In the early stages, regular eye exams are essential to monitor changes in the retina. This allows healthcare providers to detect any progression of the disease and intervene as needed.
- Control of blood sugar levels: Tight control of blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is crucial in managing diabetic retinopathy and preventing its progression.
- Laser treatment: Laser therapy, known as photocoagulation, is often used to seal leaking blood vessels and reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. This can help preserve vision and prevent further damage.
- Injection therapy: Medications called anti-VEGF drugs can be injected into the eye to help reduce swelling and block the growth of abnormal blood vessels. These injections are often used in cases of advanced diabetic retinopathy or macular edema.
- Vitrectomy: In severe cases where there is significant bleeding into the vitreous gel or tractional retinal detachment, a surgical procedure called vitrectomy may be necessary. During this procedure, the vitreous gel is removed and replaced with a clear solution to restore vision.
It’s important for individuals with diabetes to have regular eye exams to detect diabetic retinopathy early and prevent vision loss. Additionally, maintaining good control of blood sugar levels and managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol can help reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy and its complications.